MESSy is …
a software framework that combines components, which are numerical representations of our Earth system. Examples of components are atmosphere, land and ocean models, and more.
The unique feature of MESSy is a modular structure that facilitates continuous development and flexible model configurations. The concept has been established by a consortium of institutions with leading expertise in Earth System Modelling and the framework is continually further developed.
MESSy is supported by the German Climate Computing Center (DKRZ), Leibnitz Rechenzentrum (LRZ), the Max Planck Computing and Data Facility (MPCDF), the Jülich Supercomputing Centre (JSC), and the terrabyte cooperation between DLR and LRZ.
News
-

Register for the 14th MESSy Symposium
The 14th MESSy Symposium is hosted and organised by the Scientific Computing Center (SCC) of the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). The event takes place 19. – 21.05.2026 on site at the KIT Campus North, the meeting starts at 1.30 PM (with on-site registration and welcome from 12.00 PM).
-

MESSy Symposium helt in Oberpfaffenhofen
All members of the MESSy Consortium and users of the model system were invited to Oberpfaffenhofen. The 13th MESSy Symposium were helt at Deutsches Zentrum für Luft-und Raumfahrt from 24th until 26th of June 2025. Developers and users of the Modular Earth Submodel System (MESSy) met to present their latest developments and results obtained with…
-

13th MESSy Symposium 2025
We are happy to announce the next MESSy Symposium taking place 24 – 26 June 2025. We are looking forward to welcome you in Oberpfaffenhofen, seeing old and new faces and the research progress of our community. Registration for participation is open from now until 28 February 2025 via the event website: https://events.hifis.net/e/messy2025 The call…
-
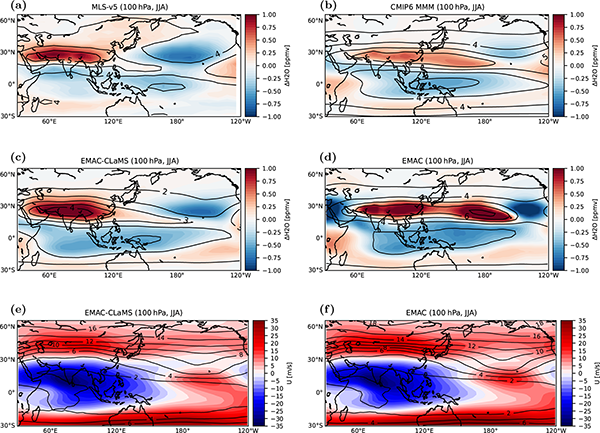
New Highlight paper by Ploeger et al. in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics
The authors present a novel mechanism of how regional anomalies in water vapour concentrations in the upper troposphere and lower stratosphere impact regional atmospheric circulation systems. These impacts include a displaced upper-level Asian monsoon circulation and strengthened prevailing westerlies in the Pacific region. Current climate models have biases in simulating these regional water vapour anomalies…
-
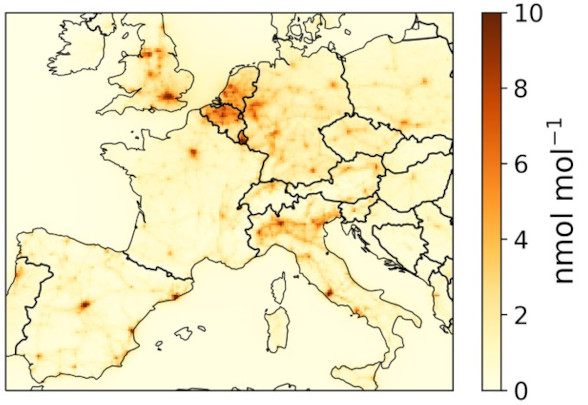
IMPAC²T – a new Young Investigator’s Group at DLR and Helmholtz Munich
The new Young Investigator’s Group IMPAC²T at DLR and Helmholtz Munich will apply the MECO(n) model system to investigate the impact of air pollution on human health and vegetation, considering climate change and the energy transition in transport. This will help to enable mobility under future climate conditions with the least possible impact on human…
Developed by the consortium of





































